Broadband 101
Broadband Toolkit Modules
- Introduction
- Module 1: Broadband 101
- Module 2: Regional & Tribal Planning
- Module 3: Data Driven Decisions
- Module 4: Find Funding
- Module 5: Bridging the Digital Divide
- Module 6: Broadband and Workforce
- Module 7: Broadband and Tourism
- Module 8: Broadband Definitions
- Module 9: Who’s Who of Rural Wisconsin Broadband
Introduction
Broadband is essential for the economic well-being of communities and is a crucial infrastructure for creating an economy for all in Wisconsin. However, expanding broadband infrastructure and maximizing broadband adoption can be complex and challenging. This toolkit aims to help economic development professionals and planners by providing a foundation for developing broadband infrastructure. It identifies key partners and resources to support communities at both local and regional levels and assists in creating tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of Wisconsin’s rural regions.
A lack of broadband access in Wisconsin stifles economic development and puts business, industry, and agriculture at a disadvantage — especially in rural areas. Prioritizing broadband expansion and working to diminish the digital divide helps our state utilize the benefits of connectivity and enables Wisconsin to reach its full potential.
bead funding in wisconsin
In 2021, The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law established the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program, aimed at ensuring high-speed internet access for all Wisconsinites. BEAD will fund the deployment of fiber and other qualifying technologies to provide a minimum service of 100 Mbps download and 20 Mbps upload to households and businesses lacking access. The BEAD program defines unserved areas as lacking download speeds of 25 and upload speeds of 3 and underserved areas lacking download speeds of 100 and upload speeds of 20. Wisconsin has been allocated $1,055,823,574, determined by a formula based on the state’s proportion of locations without broadband service, as identified using Federal Communications Commission (FCC) maps.
For more information on the Wisconsin BEAD Five-Year Action Plan and timeline for BEAD implementation, see the Internet for All webpage
Access to reliable, high-speed internet access has become a necessity of modern life. Broadband is increasingly necessary for business, education and personal use. Local, regional, and state economic development organizations throughout Wisconsin are working together to connect communities to the benefits of the internet by ensuring accurate broadband coverage through speed data, expanding coverage, and increasing affordability across Wisconsin.
Defining Broadband
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) defines broadband as having minimum benchmark speeds of 100 Megabits per second (Mbps) download and 20 Mbps upload.
The term “broadband” originates from the concept of “broad bandwidth” in telecommunications. Broadband technologies are designed to carry multiple signals simultaneously over a single communication channel or medium, utilizing a broad bandwidth. This allows for high-speed data transmission and the ability to support various services like internet access, television, and voice communication all at once. The term “broadband” became widely used as a way to distinguish high-speed, high-capacity internet services from older, slower technologies like dial-up, which had much narrower bandwidth and could only handle one task at a time.
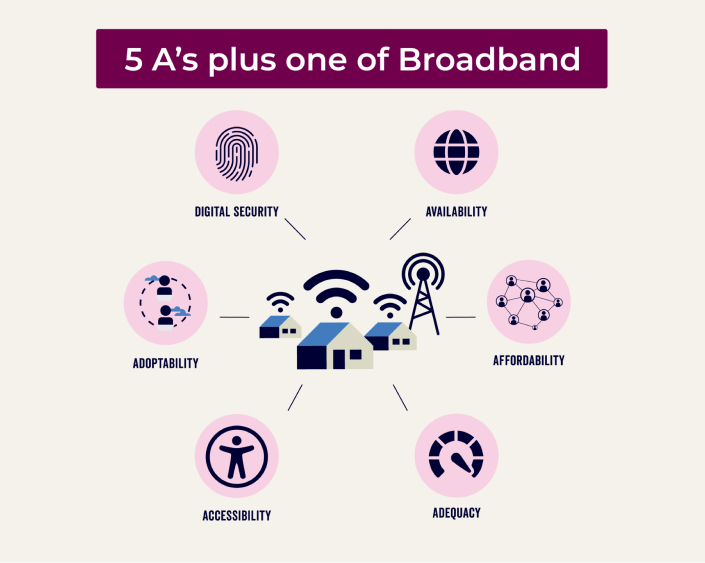
Five A’s, Plus One of Broadband
The Five A’s of broadband are a great lens to view broadband goals. Each element is important to broadband expansion and adoption. By using each A as a lens for regional planning, action steps and initiatives can be identified to resolve or enhance each core broadband issue.